About In Operating System: A Complete Guide
An Operating System (OS) is a set of system software programs in a computer that regulates the ways in which application software programs use the computer hardware application software programs use the computer hardware and the way in which users control the computer.
Introduction
All other programs require an operating system (OS) in order to launch, and the OS serves as an interface between the user and the machine. It is software that offers the user interface and regulates the internal operations of the computer hardware. When the power is switched on, it is the first software that is loaded into the computer’s memory and gives the machine a genuine start. Windows XP, Windows 10, LINUX, and UNIX are all widely used operating systems.
Features of Operating System (OS)
The features of operating system arebas follows:
- Controls and coordinates the operating of computer and input and output devices.
- Executes user programs and makes solving of. User problems easier.
- Make the Computer system convenient to use.
- Does all the interaction between user and thecomputer.
- Helps you to manage and manipulate files.
Function of Operating System (OS)
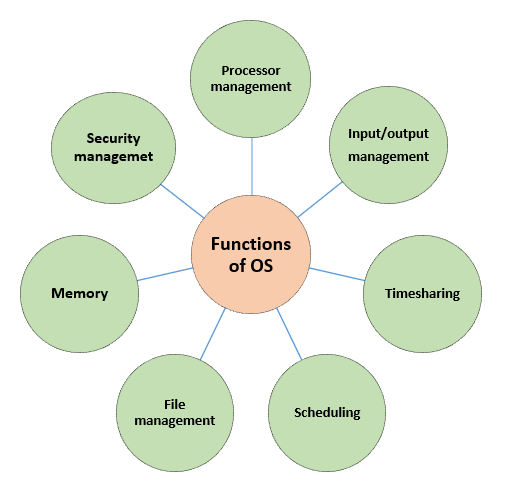
1. Management of Processes
Process creation, scheduling, and termination are managed by the operating system. By allocating CPU time and controlling process synchronization and communication, it guarantees effective execution
2. Memory Control
RAM, or primary memory, is managed by operating systems. To ensure efficient and conflict-free use, they monitor every byte, assign memory to processes, and retrieve it when it is no longer required.
3. Management of File Systems
The operating system arranges and manages drive-based data access. In addition to rights and security, it offers an organized method for managing, retrieving, and storing files and folders.
4. Input/output Management
This entails controlling input and output devices, such as disk drives, printers, and keyboards. Drivers are used by the OS to interface with hardware and facilitate data transfer between devices.
5. Security and Access Control
Operating systems enforce security through user authentication, file permissions, and activity monitoring. This protects the system and data from unauthorized access and threats.
6. User Interface Management
OS offers graphical (GUI) and command-line (CLI) interfaces that make it simple and efficient for users to interact with the system.

7. Multitasking and Job Scheduling
The OS ensures seamless multitasking and effective resource usage by setting priorities for tasks and managing several processes at once.
You also see: click The best OS
8. Networking
Many operating systems include built-in networking capabilities, allowing devices to connect and communicate over local networks or the internet.
9. Identifying and Managing Errors
Operating systems are always on the lookout for software and hardware malfunctions. To keep the system stable, they notify users and occasionally fix problems on their own.
Types of Operating System (OS)
Single User OS
It allow only one user to work on a computer at a time , e.g., Windows XP.
Multiuser OS
it allows a number of users to work together on a single computer by providing a terminal connected to a single computer e.g., Unix
It executes a single job/ program at a time, e.g., MS-DOS.
Multitasking OS
It supports the execution of more than one task at a time, e.g., Windows 2012.
Multiprogramming OS
In this, several programs can be run at the snap time via time sharing mechanism, e.g, LiNuX
Batch Processing OS
Similar types of tasking are grouped under batch and then these tasks are executed without any user interruption, e.g., MS-DOS.
Multiprocessing OS
It uses more than two CPUs within a single computer system, e.g., LINUX and UNIX.




[…] Also Read:About InternetWhat is OS […]
[…] Also Read: Hardware BasicsAlso Read: What is Operating system […]
[…] Read:Best OS for Your Desktop and LaptopWhat is Operating systemClick here to know about: CCC […]
[…] What is Computer internetWhat is Network topologyWhat is the Operating system […]