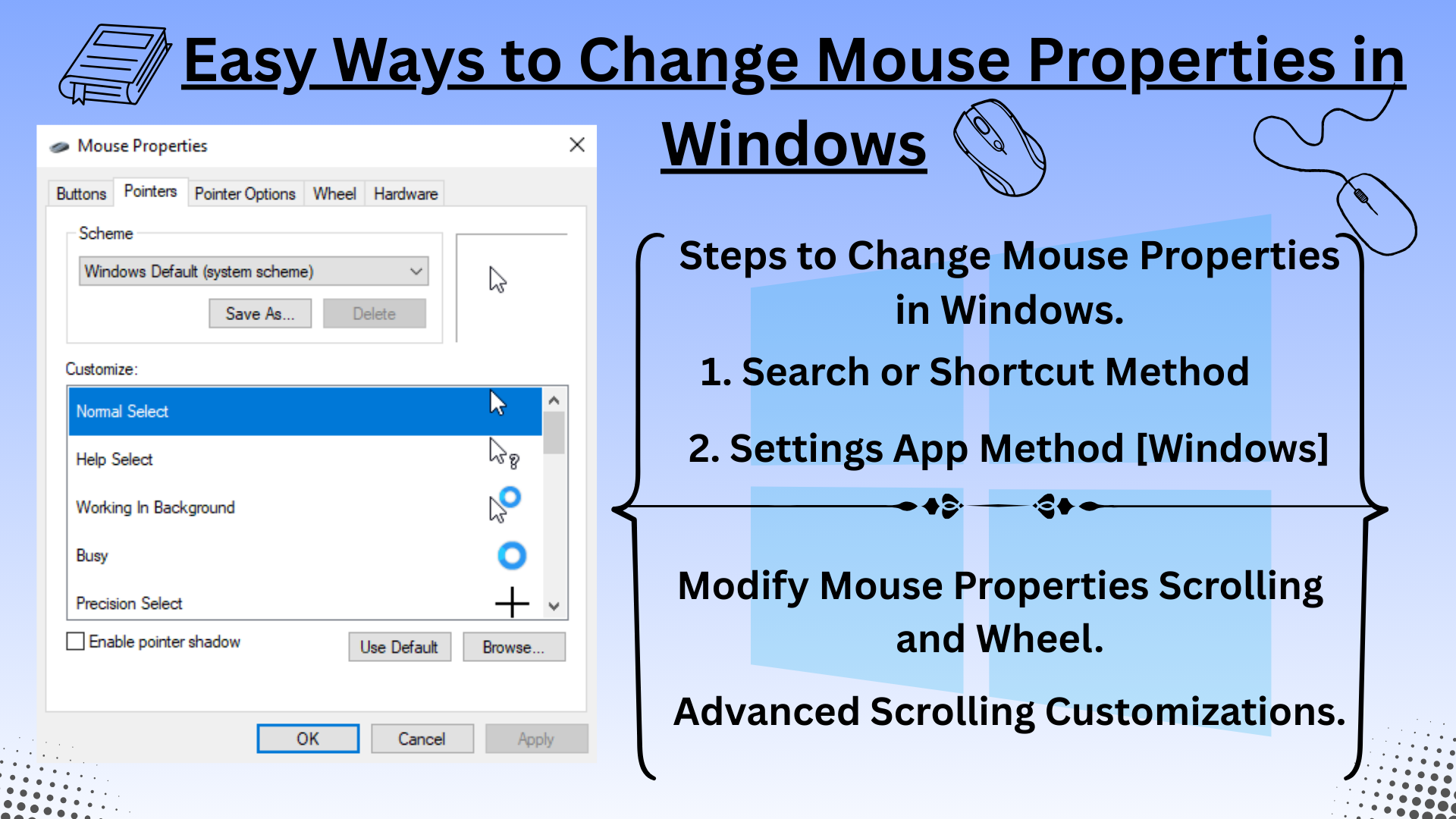
Evolution of Computer Technology: A Timeline
Evolution of Computer:
Pre-Computing Era (Before 1800s)

Abacus (circa 2400 BC): An early manual arithmetic calculating instrument.
Antikythera Mechanism (circa 100 BC): Astronomical event prediction using an old analog equipment.
Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine (1837): The basis for contemporary computing was laid by the mechanical design of a programmable computer.
First Generation Computer (1940s–1950s)

Technology: Data processing vacuum tubes.
Examples: UNIVAC (1951) and ENIAC (1945).
Characteristics: Big, unreliable, power-hungry, and programmed in machine language.
Significance: The first electrical computers that could be programmed.
Second Generation Computer (1950s–1960s)

Technology: Vacuum tubes are replaced with transistors.
Examples: CDC 1604, IBM 7090.
Characteristics: more dependable, quicker, and smaller than computers from the first generation.
Significance: High-level programming languages, such as FORTRAN and COBOL, are introduced.
Third Generation Computer (1960s–1970s)

Technology: Transistors are replaced by integrated circuits, or ICs.
Examples: PDP-8, IBM System/360.
Characteristics: quicker, smaller, and uses less energy.
Operating Systems: Multitasking operating systems were introduced.
Significance: Minicomputers and mainframes become more widely available and more reasonably priced.
Fourth Generation Computer (1970s–1990s)

Technology: microprocessors, which are single-chip CPUs.
Examples: IBM PC (1981), Apple II (1977).
Characteristics: Personal computers (PCs) become more accessible, more reasonably priced, and easier to operate.
GUI Development: The introduction of Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) (Apple Macintosh 1984, Windows 95).
Significance: introduction of the home computer and the revolution in personal computing.
Fifth Generation Computer (1990s–Present)

Technology: Cloud computing, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI).
Examples: Smartphones (like the iPhone and Android smartphones) and modern PCs.
Characteristics: combining cloud storage, mobile devices, internet access, and artificial intelligence.
Significance: Rise of the Internet Age, mobile computing, and the introduction of smart devices.
Also Read:
Computer Application in Modern Technology
What is computer
Future Trends

Quantum Computing: Quantum bits, or qubits, are used by computers to address challenging issues.
AI and Machine Learning: more developments in AI that will allow for more intelligent and self-sufficient systems.
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs): possibility for brain activity to directly operate a computer.
Neuromorphic Computing: computers that mimic the neural networks seen in the human brain.