Input Devices: Everything You Need to Know
Input Devices
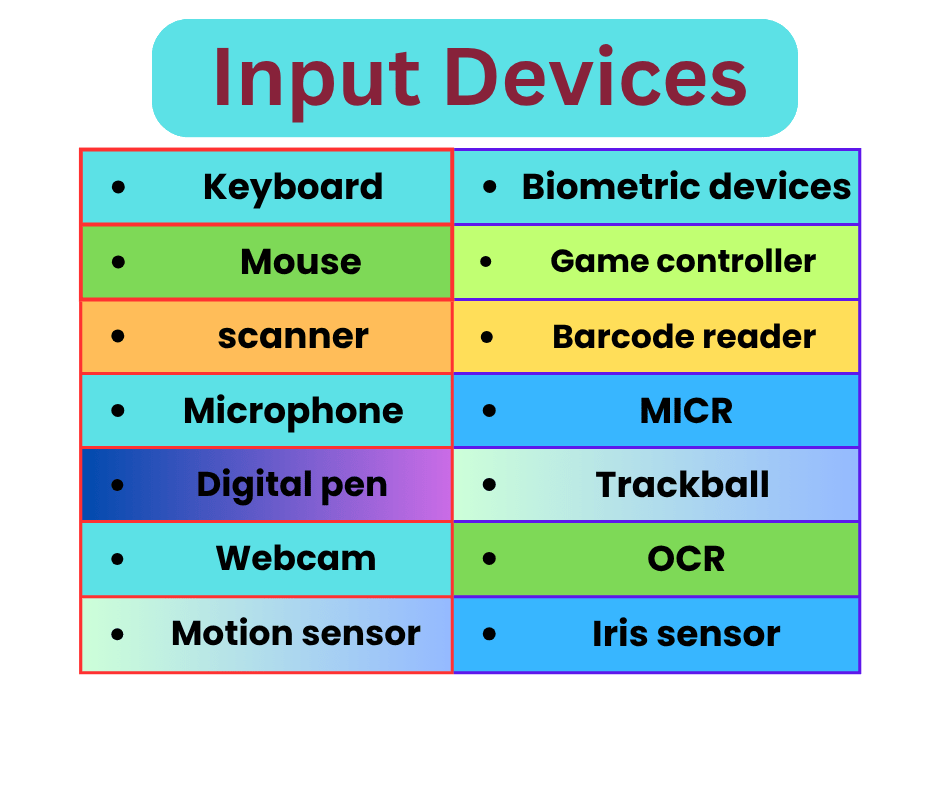
Hardware parts called Input Devices are used to communicate data or commands to a computer. They provide users the ability to communicate with the computer and supply the information needed for processing. These gadgets convert user input into information that computers can comprehend.
Keyboard
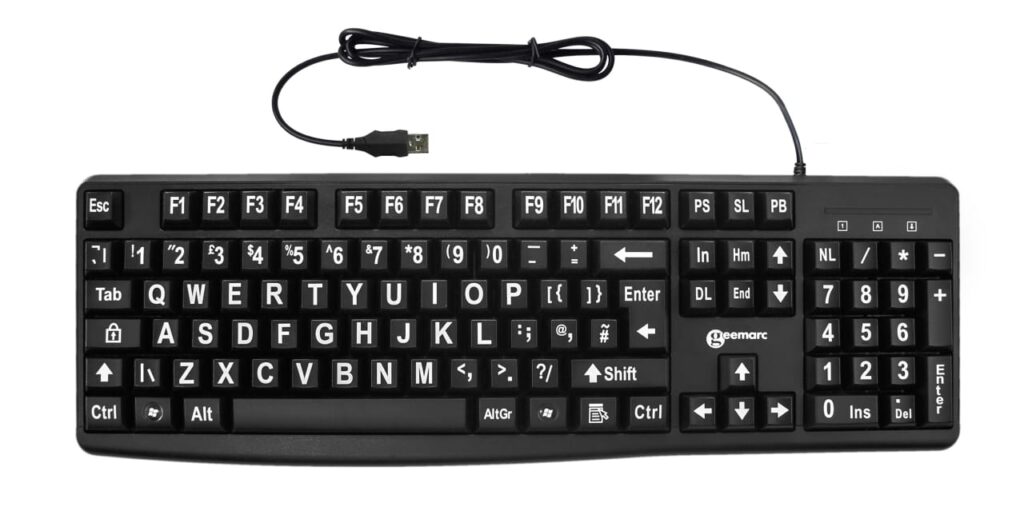

Programs and data are entered into a computer through a keyboard. It contains alphabets, digits, special characters, function keys and some control keys. When a key is pressed, an electronic signal is produced which is detected by an electronic circuit called keyboard encoder.
Types of keys on keyboard
- Function Keys (F1-F12): Make shortcuts to particular tasks available.
- Alphanumeric Keys: It includes all the numbers and letters on the keyboard. E.g. A-Z and 0-9.
- Modifier Keys: Users utilize (Shift, Ctrl, Alt) in conjunction with other keys to carry out certain tasks.
- Punctuation keys: These include Comma, semicolon and brackets.
Types of Keyboards
- Mechanical Keyboards: Make use of the physical switches beneath every key. Both gamers and typists favor them because they provide tactile feedback.
- Membrane Keyboards: Manufacturers can make key pushes quieter and less expensive by registering them with a flexible membrane.
- Ergonomic Keyboards: designed to provide a more natural typing position, hence reducing wrist and hand strain.
Mouse
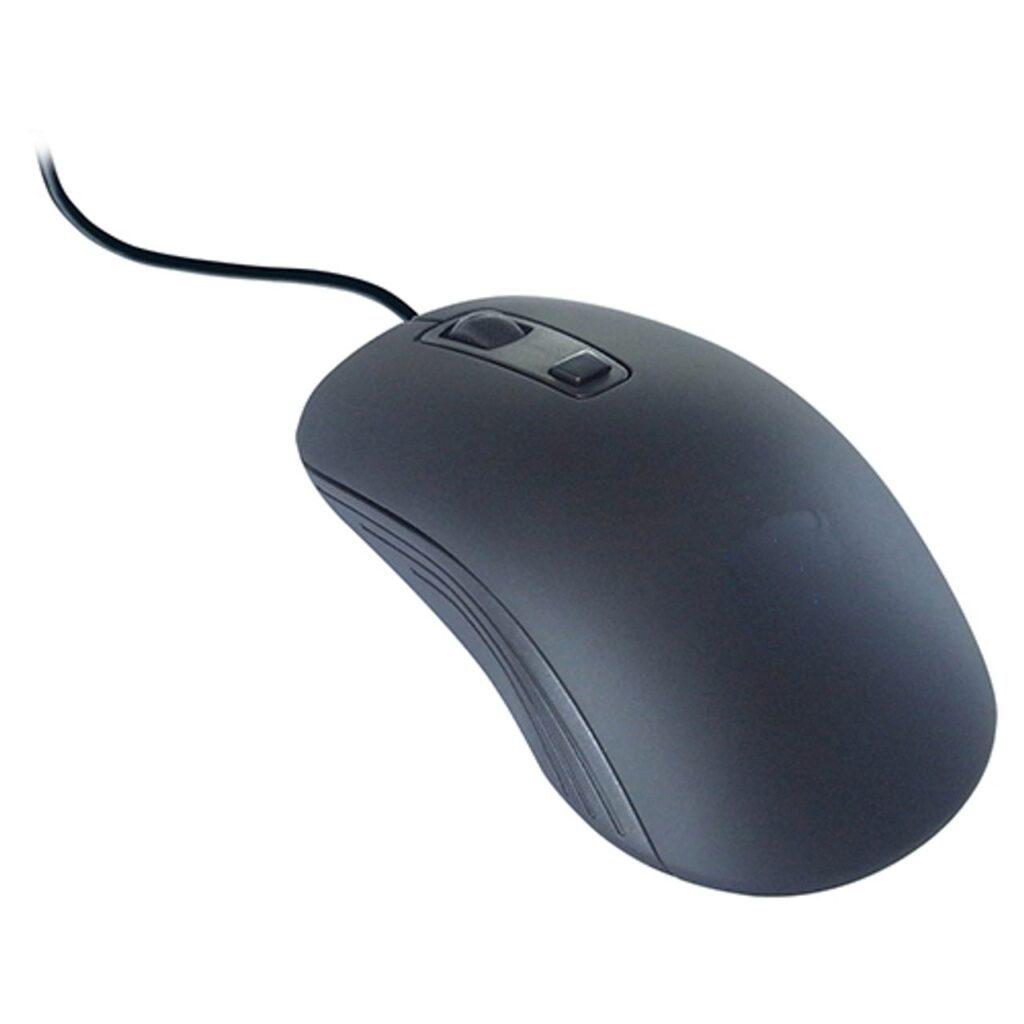

Mouse performs functions by detecting tow-dimensional motion. It is held in on hand and moved across a flat surface, generally it consists of two buttons: left and right button.
Types of Mouse
- Mechanical Mouse: Movement of cursor is relative to the movement of ball present on the bottom of mouse.
- Optical Mouse: It uses light emitting diode for detecting movement.
- Laser Mouse: Uses laser technology, which is particularly helpful for high-resolution screens, to achieve even more precision than optical mice.
- Wireless Mouse: Eliminates the need for a physical connection by communicating with the computer via Bluetooth or radio frequency technologies.
Key Features
- Buttons: often a scroll wheel and two buttons (left and right). Other buttons could offer programmed features.
- Mouse Pad: a surface that improves mouse movement, especially with optical and laser mice.
Touchpad
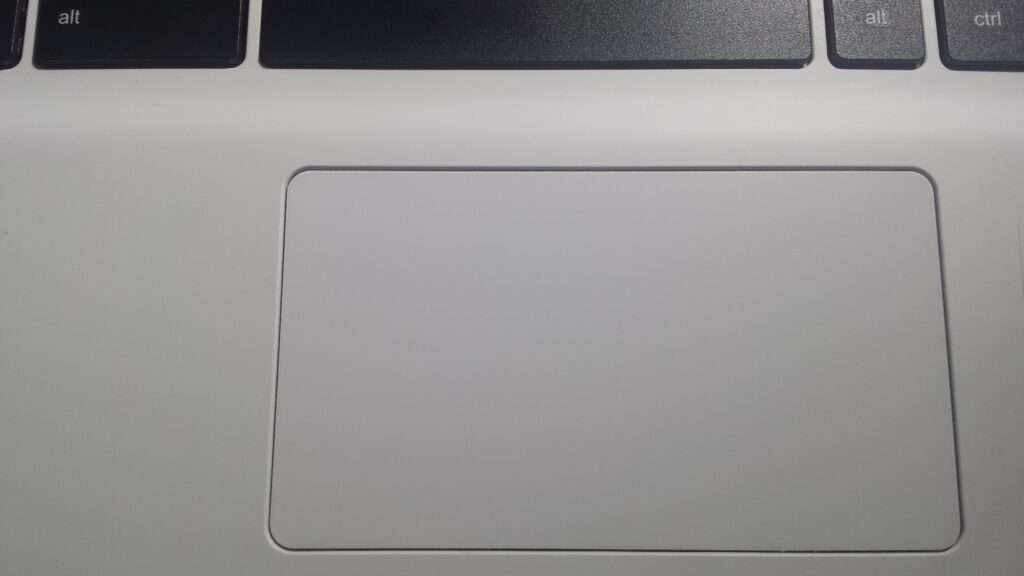

Touchpad translates motion and position of user’s fingertip to relative position on the screen. People use it in laptops.
Key Features
- Multi-touch Capabilities: enables motions such as turning, scrolling, and zooming.
- Pressure Sensitivity: Certain touchpads have the ability to sense force, allowing for various pressure-based operations.
- Alternative Names: Glide pad or trackpad.
Scanner

Information in the form of text or image entered and then transformed into digital file, which allows the computer to read or display the scanner object.
Types of Scanners
- Flatbed Scanner: The scanner takes pictures of documents that are laid out flat.
- Sheet-fed Scanner: Like flatbed scanners, but with the ability to scan many pages using an automatic feeder.
- Handheld Scanner: portable gadgets that let users physically move the scanner over objects to scan text or photos.
- 3D Scanner: creates 3D models for digital application by capturing the contour of an actual thing in three dimensions.
Key Features
- Resolution: Higher DPI (dots per inch) indicates higher-quality images.
- OCR (Optical Character Recognition): a function that can identify printed text and transform it into editable digital text.
Microphone

This input device is used to store sound in the computer with. wav as extension. In some of the laptops it is integrated inside where a microphone can be connected. It is mainly used in radio broadcasting, video conferencing sound amplifying systems, speech recognition programs and recording.
Types of Microphones
- Dynamic Microphones: Durable and suitable for a wide range of uses.
- Condenser Microphones: used for producing music or producing high-quality recordings, such as podcasts.
- Lavalier Microphones: Small, clip-on microphones are frequently used for interviews or presentations.
Key Features
- Noise Cancelling: Some microphones incorporate technology that removes background noise.
- Sensitivity: Microphones are capable of recording sound at various frequencies and sensitivity levels.
Webcam

This is a real time camera whose images can be accessed by using PC video calling application, World wide web and Instant messaging.
Types of Webcams
- Built-in Webcams: usually seen in all-in-one PCs and laptops.
- External Webcams: Professionals can access higher quality and link devices via USB or other interfaces.
Key Features
- Resolution: Higher resolution webcams, which are measured in megapixels (MP), produce images that are crisper and more defined.
- Frame Rate: Smoother video is produced by cameras that can record at a greater frame rate (FPS).
Touchscreen

It’s and electronic visual display which detects the touch within a display area. The screen sends a signal to the computer which has been touched. It works as a touch sensor, controller (PC card which translates pc understandable information), and software driver.
- Resistive Touchscreen: less sensitive but still able to sense touch using pressure (e.g., stylus, finger).
- Capacitive Touchscreen: More sensitive and responsive than resistive panels, it can detect the electrical characteristics of the human body. The majority of tablets and smartphones use capacitive displays.
Key Features
- Multi-Touch: Capacity to concurrently detect numerous points of touch, enabling pinch-to-zoom movements.
- Stylus Support: For more accurate input, certain touchscreens support the use of a pen.
Game Controllers/Joystick

A joystick is used to move the cursor continuously in the previously pointing direction on a monitor screen. It consists of a stick which pivots on a spherical boll on its base and can be moved in clockwise or anti-clockwise direction.
Types of Controllers
- Gamepads: Console- or PC-related handheld devices featuring buttons and joysticks.
- Joysticks: Usually utilized for 3D motion input in flight simulators and certain arcade games.
- Motion controllers: gadgets that sense physical motion and convert it into control of games, such as the PlayStation Move or Wii Remote.
- Steering Wheels: used to mimic real-world driving controls in racing games.
Key Features
- Analog/Digital Inputs: Digital inputs are on/off switches, but analog inputs provide continuous range of motion (e.g., pushing a button halfway).
- Vibration Feedback: To improve the game experience, a lot of controllers include tactile feedback.
Barcode Reader (Scanner)
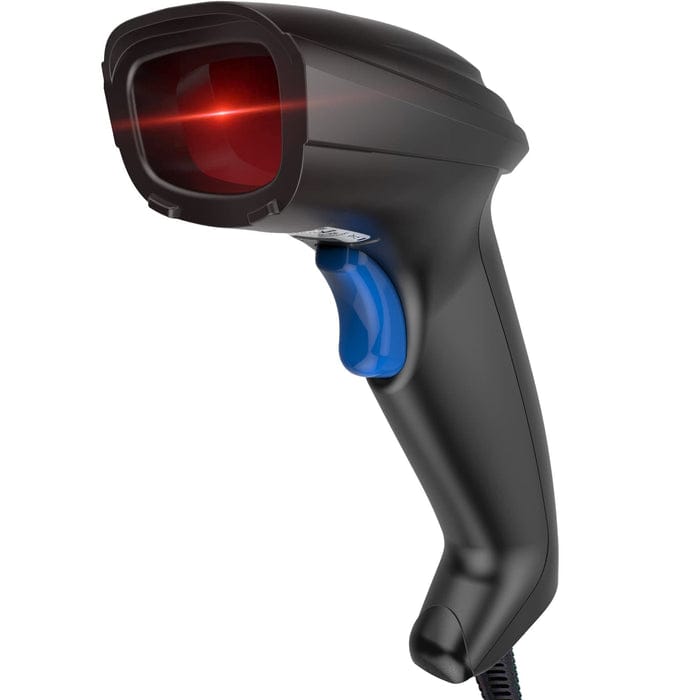

Bar-code readers are special device used to read barcoded data. barcode is a specialized code used for fast identification of items. It consist of a series of small lines, known as bars. The actual coding of the bars is the width of the bar, not of goods, such as books, postal, packaged and badges.
Types of Barcode Scanners
- Laser Barcode Scanner: reads barcodes using a laser beam.
- CCD Barcode Scanner: records barcode information using a variety of light sensors.
- Camera-based Barcode Reader: captures and decodes 2D barcodes, like QR codes, using a camera.
Digital Pen (Stylus)
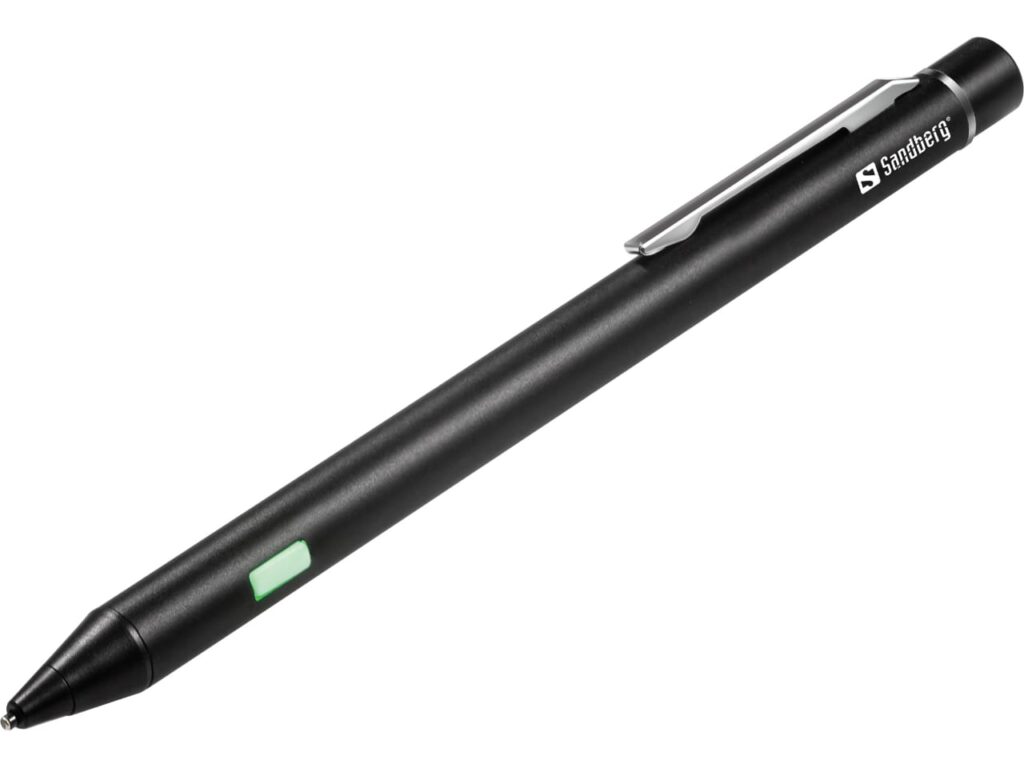

Users mainly use it to select or modify on-screen data by pointing at displayed objects or drawing on the screen. It is same as touch screen but with the greater positional accuracy. Users find it helpful in computer-aided design-like programs and very easy to use.
Key Features
- Pressure Sensitivity: Many styluses detect varying pressure, making them ideal for tasks like digital drawing or handwriting recognition.
- Tilt Functionality: Certain pens sense the angle at which users hold them, aiding in drawing or shading with graphics software.
Biometric Devices
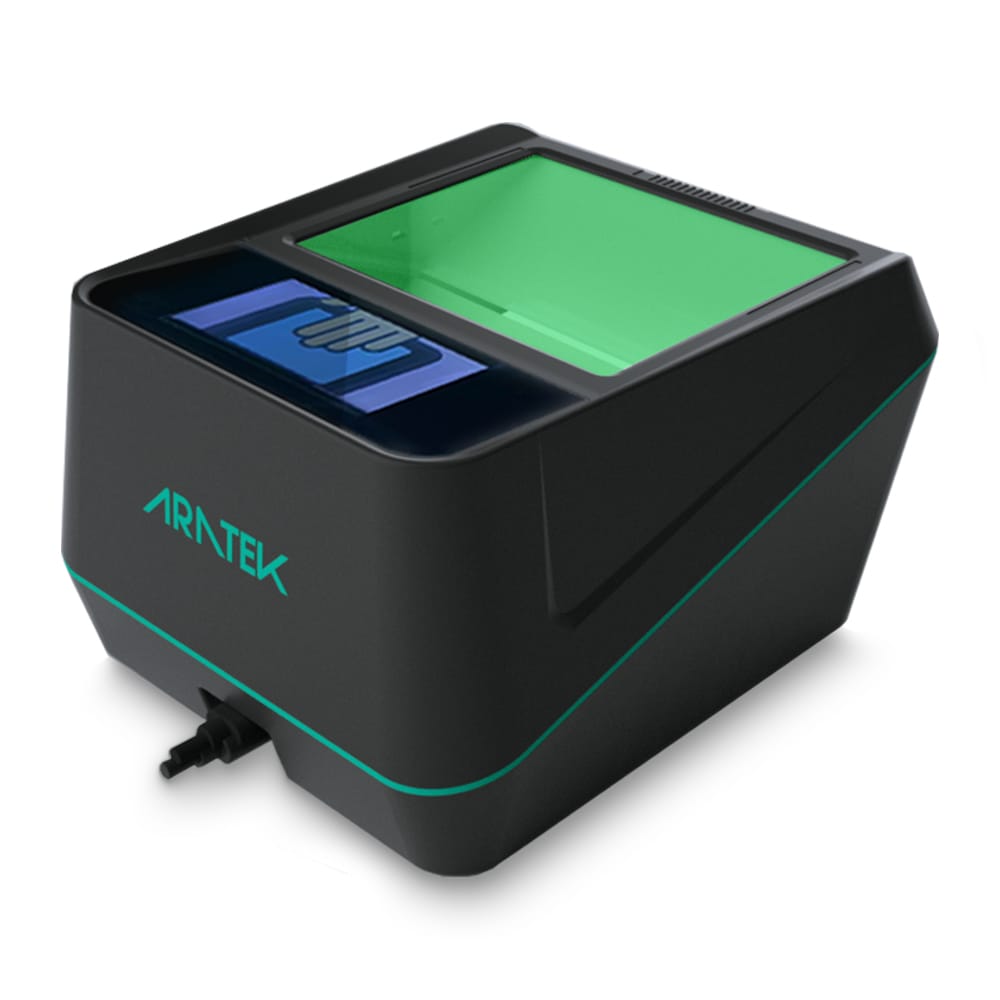

Function: used to measure biological data in order to identify and authenticate users.
Types of Biometric Devices
- Fingerprint Scanners: used to take a person’s fingerprints in order to confirm their identification.
- Facial Recognition Systems: Examine facial traits to verify who you are.
- Iris Scanners: For safe authentication, look for distinctive patterns in the eye’s iris.
Key Features
- Security: airports, protected equipment, and other locations requiring sensitive access frequently utilize high security.
- Accuracy: Due to their great accuracy, organizations widely use several biometric methods for authentication.
Trackball
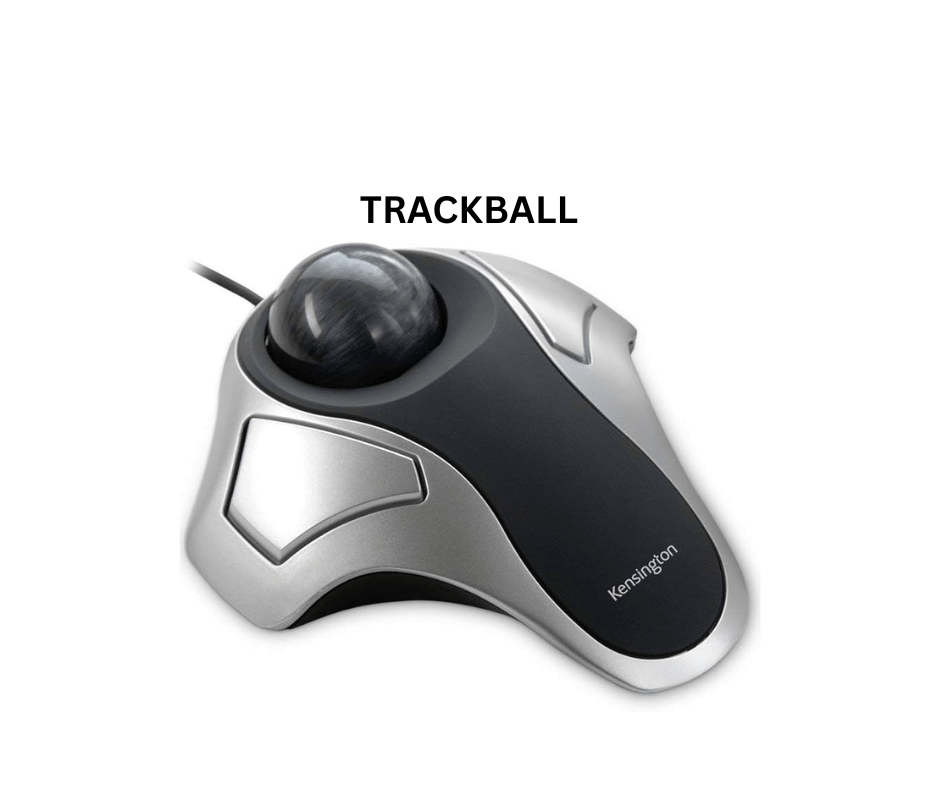

Users roll the ball on its top with a finger. They widely use it in CAD workstations, radar consoles in air traffic control rooms, and sonar equipment on a ship.
OCR
OCR- Optical character reader/recognition. It is new technology that helps in reading the characters form printer paper into a computer by recongizing the shape of character through light source and photoelectric cell.
OCR software converts the page into typed form, enabling users to edit it in any text editor.
MICR

MICR- Magnetic ink character reader/ recognition. It is mainly used in banking industry to facilitate the processing of cheques by allowing computers to red information like account number form the printed documents.
Usually iron oxide magnetic toner or ink is used to print the MICR characters are magnetize by decoding a MICR text and then it is passed over and MICR read head. This produce a waveform that can be easily process by the system
Motion sensor

An electronic gadget that recognizes movement in a particular region is called a motion sensor. It is frequently utilized in automation, energy-saving applications, and security systems.
Iris scan

A biometric tool called an iris scanner uses a person’s unique irise patterns—the colored ring surrounding the pupil—to identify them. It employs near-infrared light to take high-resolution pictures of the irises, which are subsequently compared to templats that have been stored for identification or authentication.




I learned something new today. Thanks for sharing such valuable information