Network Protocol: A Complete Information
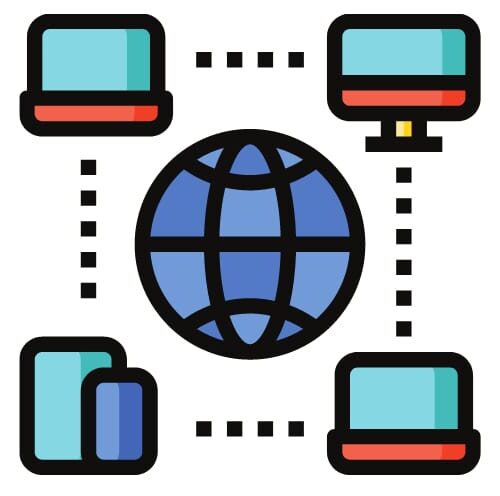
What is a network protocol?
The rules and guidelines that specify how data is sent and received via a network are known as a network protocol. These protocols guarantee dependable and effective communication between devices made by various vendors.
Types of Network Protocol
- IP (Internet Protocol)
- TCP(TransmissionControl Protocol)
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
- FTP (File TransferProtocol)
- POP ( Post Office Protocol)
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
- Enthernet
- wi-Fi
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
- Gopher
- Telnet
Internet Protocol (IP)
Purpose: transports data packets from their origin to their final location.
Versions: IPv4 (32-bit) and IPv6 (128-bit).
How it works: gives devices IP addresses, which are then used to forward traffic.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
Purpose: Quick, error-free transmission without a connection.
Used in: Streaming, online games, VoIP.
See more :
What is Computer internet
What is Network topology
What is the Operating system
Features:
- No guarantee of delivery
- Low latency
- Lightweight protocol
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP / HTTPS)
Purpose: moves web pages from a client to a server.
HTTPS: Secure version with encryption via SSL/TLS.
Used in: Browsing websites, web apps.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
Purpose: Transfers files between a client and server.
Secure Variants: FTPS, SFTP.
Commands: GET, PUT, LIST.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
Purpose: Sends emails.
Works with: POP3 or IMAP to retrieve emails.
Secure version: SMTPS (uses SSL/TLS)
Post Office Protocol (POP3) and Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
POP3: removes emails from the server after downloading them.
IMAP: maintains email synchronization between devices and on the serverDynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Purpose: gives networked devices their IP addresses automatically.
How it works: When a client submits a request, the DHCP server responds with configuration details.
Domain Name System (DNS)
Purpose: Translates human-readable domain names (like google.com) into IP addresses.
Works like: A phone book for the internet.Secure Shell (SSH)
Purpose: safely connects to distant PCs over a network.
Used by: system managers for managing servers remotely.Protocol Stack (TCP/IP Model Layers)
Application Layer – Apps and services (HTTP, FTP, SMTP)
ransport Layer – Reliable delivery (TCP, UDP)
Internet Layer – Addressing and routing (IP)
Network Access Layer – Physical transmission (Ethernet, Wi-Fi)Why Are Network Protocols Important?
Interoperability: Devices from many suppliers are able to exchange information.
Efficiency: specifies the amount, frequency, and format of the data.
Security: Protocols like HTTPS and SSH encrypt communication.
Scalability: Standard protocols allow easy expansion of networks.
You can also read : Advantage of Computer In Modern Life



[…] Also Read:About in network protocol […]
[…] See More : About In Network Protocol […]