Output Devices: Everything You Need to Know
Output Devices
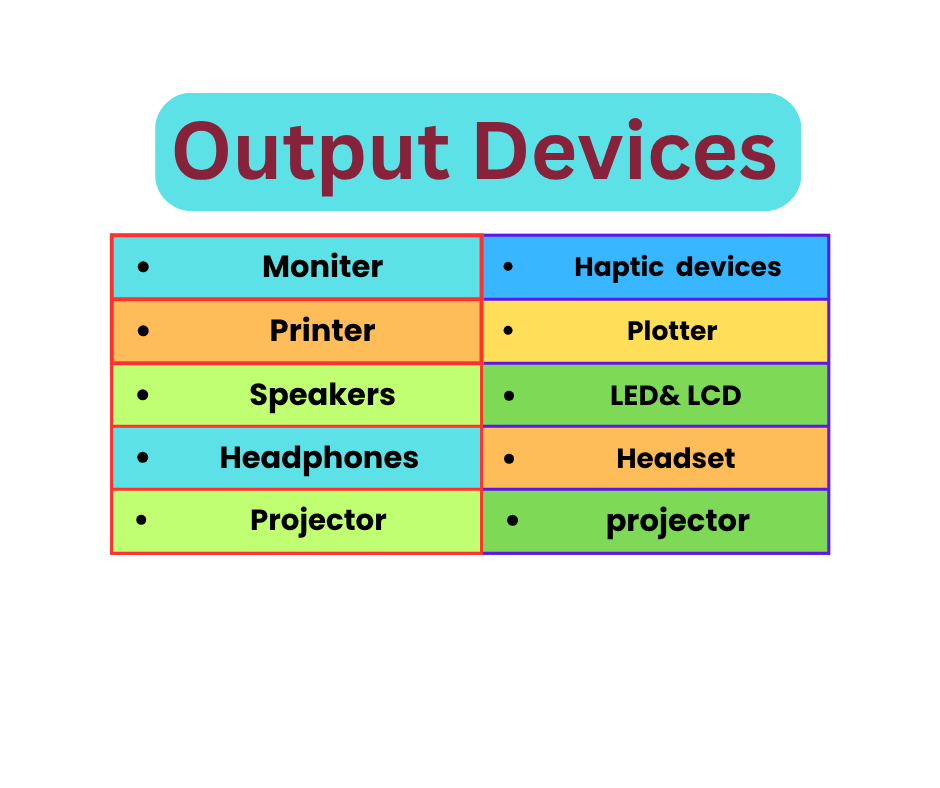
Hardware components known as Output Devices are used to show or present computer-processed data in a way that is both machine-readable and human-readable. In contrast to input devices, which let people provide the computer data, Output Devices let the computer give information, results, or feedback.
Monitor (Display Screen)
It is a most common output device that is also know as electronic visual display or visual display unit for computer. The output is display on screen and there are number. Of pixels or small dots that. Make a picture display on monitor the displayed output is a soft copy.

Types of Monitors
- CRT (Cathode Ray Tube): The most commonly used monitor consists of an electron gun that emits a beam of electrons to light up the phosphor dots.
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display): This comes in existence after the CRT monitor that are lighter in weight and thinner than CRT monitors. It used liquid crystals’ light-modulating properties to save lots of space and provide wide viewing angles.
- LED (Light Emitting Diode): Light-emitting diodes make up these monitors and offer better display quality and color compared to other types of monitors. These monitors are light in weight, thinner and flatter.
- OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode): Better contrast and color reproduction are made possible by biological components that make up each pixel, which generate light when electric current flows through them.
- Touchscreen Monitors: Users interact with the display by touching it because it functions as both an input and output device.
Key Features
- Resolution: measured in pixels, such as Full HD’s 1920×1080 resolution. Images with higher resolution are crisper.
- Refresh Rate: The frequency at which the screen image is updated (e.g., 60Hz, 120Hz). Smoother graphics are provided by a greater refresh rate, which is crucial for video or gaming.
- Size: From tiny displays to enormous ones ideal for professional workstations, gaming, or entertainment, monitors are available in a variety of sizes.
- Aspect Ratio: the screen’s width to height ratio, which for the majority of contemporary displays is 16:9.
Printer
The printer produces a hard copy of documents, storing them in an electronic form on physical print media.
Types of Printer

Impact Printer
- Dot matrix printer: It uses a print head that runs back and forth, or in an up and down motion, on the page and prints by impact, striking an ink-soaked cloth ribbon against the paper.
- Daisy-wheel printers: It uses a wheel as a print head, which rotates, and then the hammer strikes on the backside of the spoke and presses it against the paper to print a character. They cannot produce high-quality print graphics.
- Line printers: It is a high-speed printer, which prints an entire line at a time. It produces a lot of noise.
- Drum printers: A drum printer prints character images around a cylindrical drum.
Non-Impact Printer
- Laser Printers: These printers print one page at a time and use lase light source to produce and image on a photosensitive drum.
- Electromagnetic printer: These are fast printer, fall under the category of page printer.
- Thermal printer: Thermal printers often deliver poor print quality, and paper is widely used in battery-powered equipment.
- Electrostatic printer: Digital printers are used for printing large images quickly, which reduces costs.
- Inkjet printer: It fires droplets of ink on paper to create the text impression as its print head contains tiny nozzles of different color
Key Features
- Print Speed: in pages per minute (PPM) units. Inkjet printers are usually slower than laser printers.
- Resolution: Measured in dots per inch (DPI), the higher the DPI, the sharper the print quality.
- Connectivity: For convenient printing from PCs, smartphones, and tablets, printers may be connected by Bluetooth, USB, or WiFi.
Speakers
Speakers emit voice, music, or sound from the computer to provide aural feedback or amusement.

Types of Speakers
- Wired Speakers: Use an HDMI cable, USB, or 3.5mm jack to connect to the computer.
- Wireless Speakers: Connect to the computer via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi for greater flexibility and fewer wires.
- External Sound Systems: High-end speaker systems are frequently utilized for professional audio applications or home theater surround sound.
Key Features
- Sound Quality: measured using frequency response, which establishes the sound’s depth and clarity.
- Volume and Bass: For music and games, speakers can have different sound output levels (measured in watts) and bass augmentation.
- Surround Sound: For a more engaging experience, surround sound features may be available with more sophisticated speaker systems.

Headphones
A device delivers personal audio output by putting sound straight into the user’s ears. People frequently use it for audio activities such as gaming, video chats, and listening to music.
Types of Headphones
- Wired Headphones: Use a cable to connect to the computer (usually a 3.5mm jack, USB, or Bluetooth).
- Wireless Headphones: To increase mobility, connect to the computer using Bluetooth or another wireless technology.
- Noise-Cancelling Headphones: Utilize technologies to cut down on or eliminate background noise for a more engaging listening experience.
- In-Ear Monitors (IEMs): For high-quality sound, artists and audio professionals usually utilize tiny, in-ear headphon
Key Features
- Wired Headphones: Use a cable to connect to the computer (usually a 3.5mm jack, USB, or Bluetooth).
- Wireless Headphones: To increase mobility, connect to the computer using Bluetooth or another wireless technology.
- Noise-Cancelling Headphones: Utilize technologies to cut down on or eliminate background noise for a more engaging listening experience.
- In-Ear Monitors (IEMs): For high-quality sound, artists and audio professionals usually utilize tiny, in-ear headphones.
- Key Features:
- Sound Quality: Headphones are assessed according to frequency response and sound clarity, just like speakers.
- Comfort: With different levels of comfort, moreover, headphones are available in over-ear, on-ear, and in-ear styles.
- Microphone: For gaming or video chats, some headphones come with built-in microphones.
Projector

Frequently used for presentations or entertainment, a projector projects computer output—such as pictures, movies, and presentations—onto a larger surface, such as a wall or screen.
Types of Projectors
- LCD Projectors: Project pictures using liquid crystal display technology. They are frequently employed in professional or academic contexts.
- DLP Projectors (Digital Light Processing): Project pictures using a digital micromirror device (DMD). Compared to LCD projectors, they are smaller and create crisper pictures.
- LED Projectors: Use LED light sources, which have a longer lifespan and higher color accuracy.
- Laser Projectors: Make use of laser technology, which has greater colors, more brightness, and a longer lifespan than conventional projectors.
Key Features
- Resolution: Like monitors, projectors can have various resolutions (1080p, 4K, etc.) to produce sharper images.
- Brightness: Brighter visuals are indicated by higher lumens, which are measured. When utilizing projectors in well-lit spaces, this is essential.
- Throw Distance: The size of the projected picture is determined by the distance between the projector and the screen.
Virtual Reality (VR) Headset
A device that outputs computer-generated visuals, sound, and sometimes tactile feedback to immerse the user in a virtual environment. Used in gaming, simulations, and training.

Key Features
- Immersive Experience: With the help of 360-degree images and spatial audio, virtual reality headsets give users the impression that they are in a virtual environment.
- Motion Tracking: VR headsets follow the motions of the user’s head and body to modify the virtual world as necessary.
- Resolution and Refresh Rate: To minimize motion sickness and guarantee a seamless experience, high resolution and refresh rate are essential.
Haptic Devices

By using movements or vibrations to mimic the sensation of touch, you may provide consumers tactile feedback. frequently employed to provide a more immersive experience in simulations or games.
Examples
- Game Controllers with Haptic Feedback: In order to replicate in-game occurrences, many contemporary gaming controllers (such as PlayStation’s DualSense) come with built-in motors that vibrate or give resistance.
- Vibration Chairs and Suits: Wearable technology that offers tactile input is frequently employed in virtual reality or simulation-based applications.
Key Features
- Vibration: gives tactile feelings, such as resistance or bumps.
- Force Feedback: Like maneuvering a car in a racing game, certain gadgets can replicate the feeling of force or resistance.
Plotter

The computer uses these to produce precise and high-quality graphics and drawings by controlling an ink pen or inkjet.
Types of Plotters
- Drum plotter/Roller Plotter: It consists of a roller on which a paper is placed, and th cechanical device known as robotic Drawing Arm, moves side to side as the paper anre rolled back an dforth through the roller.
- Flatbed Potter/Table Plotter: It contains a long stationar horizontal surface on which the paper is fixed , and the pen is allowed to move along the horizontal and vertical axis.
- An electrostatic plotter is a kind of large-format printer that prints images on paper using an electrostatic technique. Other names for it include an electrostatic printer and a drum plotter.
Key Features
- Resolution: Designers intended the sign to be visible in public areas or from long distances.
- Size: Plotters are appropriate for applications in engineering, architecture, and design since they can produce enormous pictures.
LED & LCD Displays
Specialized displays, such as those used in car dashboards, digital signs, and ads.

Types
- LED Signs: Typically used for large-scale displays or signage (e.g., billboards).
- OLED Displays: frequently used in digital signage to provide crisper, brighter images.
Key Features
- Size and Clarity: Designers intended it to be seen in public areas or across long distances.
- Durability: designed to endure and resist a range of climatic conditions.




[…] computer network is a system that allows computers, servers, printers, and other computing devices to interact and share resources. These networks can be as simple as linking two devices or as big […]