Dictionary Programs in Python: Important for O Level

Dictionary Programs in Python: A dictionary in Python is a collection of key-value pairs. It is one of Python’s core built-in data types and is mutable and indexed by keys.
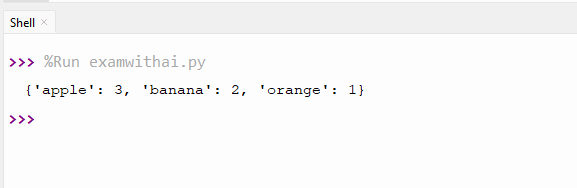
1. Write a program to count the frequency of elements.
CODE
data=['apple','banana','apple','orange','banana','apple']
freq={}
for item in data:
freq[item]=freq.get(item,0)+1
print(freq)OUTPUT
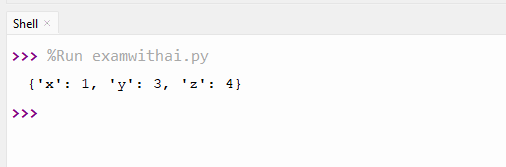
2. Write a program to merge two dictionaries.
CODE
a={'x': 1, 'y': 2}
b={'y': 3, 'z': 4}
merged={**a, **b}
print(merged)OUTPUT
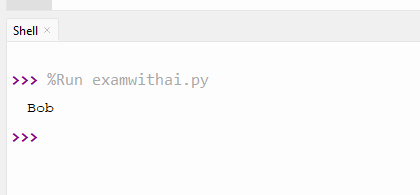
3. Write a program to find the key with the maximum value.
CODE
scores={'Alice':88, 'Bob':95, 'Charlie':91}
max_key=max(scores,key=scores.get)
print(max_key)OUTPUT
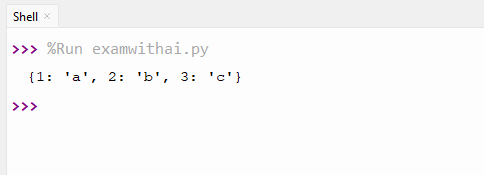
4. Write a program to invert a dictionary.
CODE
original={'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
inverted={v:k for k, v in original.items()}
print(inverted)OUTPUT
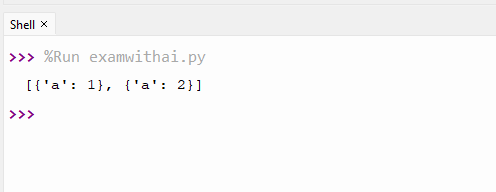
5. Write a program to remove duplicates from a list of dicts.
CODE
import json
data=[{'a':1},{'a':2},{'a':1}]
unique=list({json.dumps(d): d for d in data}.values())
print(unique)OUTPUT
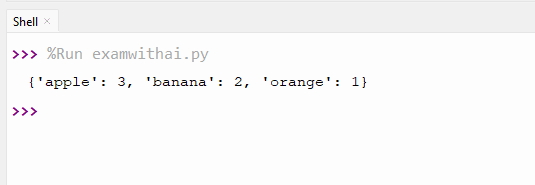
6. Write a program to count words in a string.
CODE
text="apple banana apple orange banana apple"
words=text.split()
count={}
for word in words:
count[word]=count.get(word,0)+1
print(count)OUTPUT
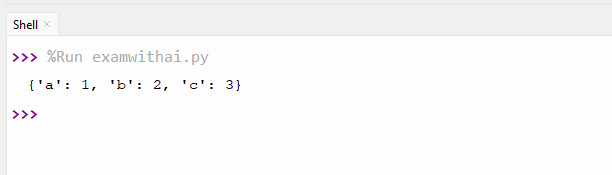
7. Write a program to convert two lists into a dictionary.
CODE
keys=['a','b','c']
values=[1,2,3]
combined=dict(zip(keys,values))
print(combined)OUTPUT
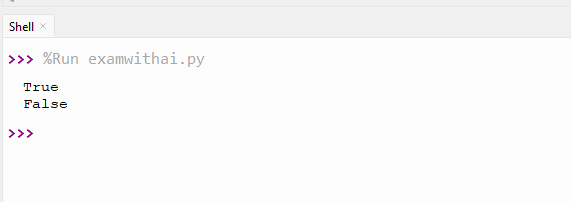
8. Write a program to check if a key exists.
CODE
d={'a':1, 'b':2}
print('a' in d)
print('c' in d)OUTPUT
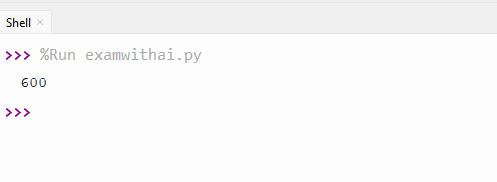
9. Write a program to sum the dictionary value.
CODE
nums={'a': 100, 'b':200, 'c':300}
total=sum(nums.values())
print(total)OUTPUT
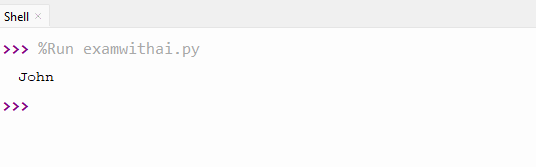
10. Write a program for nested dictionary access.
CODE
data={'person':{'name':'John','age':30}}
print(data['person']['name'])OUTPUT