The Internet: A Complete Explanation & Guide
Introduction of Internet
Computer communication means communication between the computers or data transmission from one computer to another computer. The Internet has been in a state of continuous evolution since the late 1960s. Some simplified description of the Internet, are “a large computer network” or “network of networks “” “an instantaneous and global messaging system”. Internet is an immensely complex combination of thousands of technologies and dozens of services use by tens of millions of people around the world each day. Every network and every computer in these network exchange information according to certain rules called protocols. These different computers and different network are united with the common thread. Of two protocol, I.e., Internet Protocol (IP) and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP).
The History of the Internet:
- The Internet took time to emerge. It began in the late 1960s and developed across several decades:
- ARPANET (1969):
Almost created by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the U.S. Department of Defense, ARPANET was the first actual forerunner of the Internet. It was created to enable information sharing amongst researchers over a computer network. The system crashed after the first two letters (“LO” of “LOGIN”) in the first message ever delivered, which was between UCLA and Stanford. - Vint Cirf and Bob Kahn:
The “Father of the Internet” is usually acknowledged to be Vint Cerf, along with Bob Kahn. Both performed major roles in designing the TCP/IP protocol, which is the foundation of how data is transported throughout the Internet.
TCP/IP Protocol is Born (1970s):
One significant turning point was the creation and uptake of the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) in 1983. It laid the foundation for the current Internet by enabling communication and connection between many networks.
Types of Internet Paths
Wired Path
- makes use of physical wires, such as Ethernet, coaxial, or fiber optics.
- provides data transfer that is quicker and more reliable than wireless.
- foundation of the international Internet system.
2. Wireless Path
- uses radio waves rather than wires.
- prevalent in satellite connections, 4G/5G mobile networks, and Wi-Fi.
- may encounter delays as a result of interference or a weak signal.
3. Satellite Path
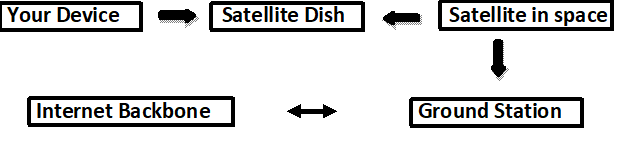
- You ask your device for information, such as when you access a webpage or video.
- A satellite dish at your location—on your home, ship, aircraft, etc.—receives the signal.
- The signal is transmitted from the dish to a satellite in orbit.
- A ground station on Earth that is linked to the Internet backbone receives the signal from the satellite.
- The data, such as a YouTube video, is retrieved by the ground station from the Internet.
You can also read : About The Computer internet
Positive Effects of Internet On Global
Almost every element of life has been drastically changed by the Internet:
Communication
- Real-time global communication is now simple thanks to video calls, instant messaging, and email.
- Social media sites like Instagram, Twitter, and Facebook link billions of people together.
Education
- Like a top universities provide courses on online learning platforms.
- Thanks to search engines like Google, information is now more easily accessible.
Business and Economy
- Amazon, Alibaba, and other e-commerce sites have transformed the way we shop.
- Global freelancing and remote employment have grown in popularity, particularly since the COVID-19 epidemic.
Society and Culture
- Today, virtual realities, online communities, and digital cultures have all emerged as a result of the Internet.
- Nowadays, people consume media and news online, enabling citizen journalism and real-time updates.
Also Read:About in network protocol
Challenges and Concerns
- Cybersecurity threats -ike hacking, phishing, and data breaches.
- Privacy issues with companies collecting user data.
- Misinformation and fake news are spreading rapidly.
- Digital divide, where some parts of the world still lack reliable Internet access.



[…] Also Read: About the Internet […]
[…] Also read: Output DevicesAlso read: About the Extensions file Also read: What is internet […]
[…] Read: Input DevicesAbout the InternetWhat is softwareWhat is […]
Informative article for me
Thank you. Stay connected with us.